Intravital
Microscopy
Intravital microscopy (IVM) is an advanced optical imaging technique that allows scientists to visualize and analyze cellular behavior within a living organism in real time. Unlike conventional microscopy, IVM provides a dynamic, high-resolution view of biological processes in their natural, complex environment.
This technology uses various microscopy techniques, such as confocal or two-photon microscopy, combined with specialized animal models (like mice with surgically implanted 'imaging windows' that provide a stable, long-term view of a tissue).
Fluorescent dyes and genetically engineered fluorescent proteins are used to label specific cells, such as cancer cells or immune cells, making their movement and interactions visible.
Partnership
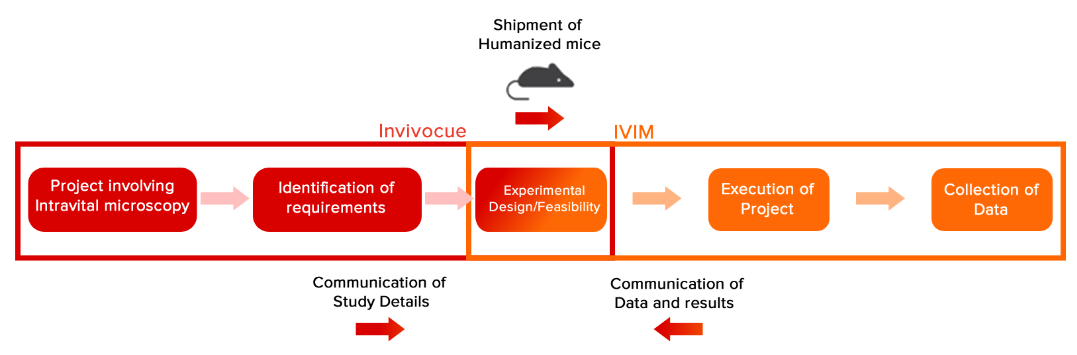
Invivocue has partnered with IVIM Technology to offer a combined technology platform incorporating humanized mice and intravital microscopy. By combining our expertise in humanized mouse models and disease areas with IVIM's cutting-edge IntraVital Microscopy (IVM) platforms, Invivocue is able to offer unparalleled insights into disease mechanisms and drug efficacy at the cellular level.
Through our partnership with IVIM Technology, we're able to offer tailored intravital microscopy services combining the benefits of Invivocue's humanized mice and disease-specific domain knowledge, accelerating your drug discovery pipeline.
Workflow
In Vivo Labeling Technology - IVI Tag™
IVI Tag™ is an in vivo reagent that tracks cellular mechanisms and tissue proteins in living animal organs by binding to them specifically. Developed with IVIM Technology's advanced fluorescence tagging, it surpasses traditional antigen-antibody methods by precisely expressing fluorophores.
HiMice and Intravital Microscopy applications
In oncology, the tumor microenvironment (TME) is of great interest because it is a critical factor in cancer development, progression, and treatment resistance.
By combining the immune system of HiMice and IVM, humanized immune system responses in the TME can be tracked longitudinally.
Tumour adaptation, immune cell exhaustion, immune evasion and metastasis are some of the key insights that can be observed using our combined technology approach.
Autoimmune disorders feature a maladaptive response to an external insult, and can be triggered by sources such as viruses, infection, diet and many more.
Intravital microscopy opens a window into the complex pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus eythematosus (SLE) on as it progresses.
The gradual onset of human immune cell autoantibody production, cytokine release and the process of antigen presentation are some possible areas of investigation.
Understanding certain human-specific infections require humanized cells, such as liver cells found in invivocue's HepMice.
By combining Invivocue's HepMice and IVM, infection, pathogenesis and treatment response to Hepatitis B virus can be observed in real-time.
This allows for the development of effective therapeutic strategies that focus on viral clearance or anti-inflammation.
Abstract: To examine the application of an immune checkpoint inhibitor targeting PD-1 in the 4T-1 xenograft animal model. PD-1, present on the surface of T cells, binds to its ligand and prevents T cells from attacking cancer cells. Byblocking PD-1, the aim is to uncover the mechanisms of immune enhancement in immunotherapy within the tumor microenvironment (TME).
Example Experiment
Experimental Design
Data
The observed dynamic dendritic cell infiltration rate correlated with the growth of breast cancer cells, indicating an adaptive real-time response to tumor progression. This was also accompanied by peak T cell activation on the third day, followed by a decline thereafter.
Videos
Intravital microscopy capabilities
Intravital microscope technology